148. 排序链表
在 O(nlogn) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序。
示例 1:
1
2
| 输入: 4->2->1->3
输出: 1->2->3->4
|
示例 2:
1
2
| 输入: -1->5->3->4->0
输出: -1->0->3->4->5
|
思路:
因为时间复杂度是O(nlogn),所以就会想到归并排序,但是常数级空间复杂度又限制了不能采用递归,因此:
定义了三个函数:
-
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head):用于进行归并排序
-
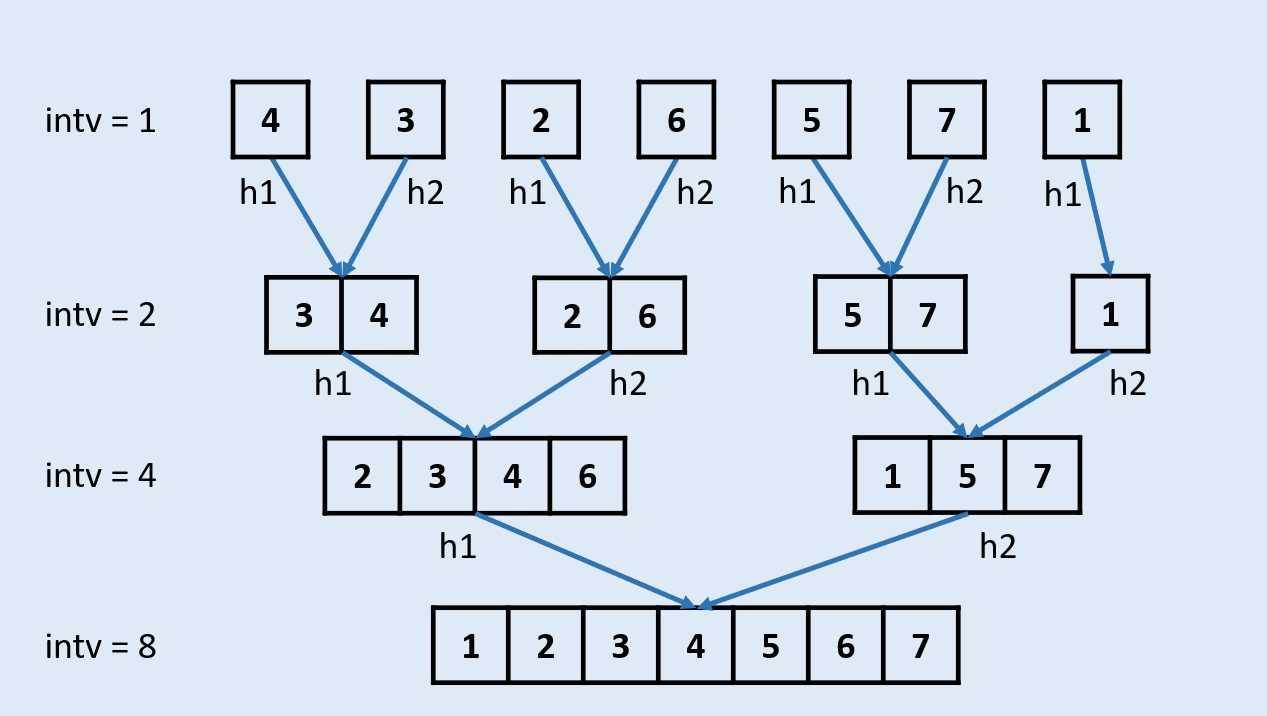
ListNode* cut(ListNode* head, int size): 用于拆分,从head节点开始,拆分size长度,即进行如下图的操作:

-
ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2):应该是闭着眼睛都会写的,归并两个有序链表。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
|
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
int length = 0;
ListNode* tempH = new ListNode(0);
tempH->next = head;
ListNode* lenP = head;
while(lenP) {
length++;
lenP = lenP->next;
}
for(int size = 1;size < length;size <<= 1) {
ListNode* H = tempH;
ListNode* cur = H->next;
while(H->next) {
ListNode* left = cur;
ListNode* right = cut(left, size);
cur = cut(right, size);
H->next = merge(left, right);
while(H->next) {
H = H->next;
}
H->next = cur;
}
}
return tempH->next;
}
ListNode* cut(ListNode* head, int size) {
ListNode* temp = head;
while(--size && temp) {
temp = temp->next;
}
ListNode* last = temp;
if(!temp) {
return NULL;
}
temp = temp->next;
last->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* temp = head;
while(l1 && l2) {
if(l1->val < l2->val) {
temp->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
} else {
temp->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
temp->next = l1 ? l1 : l2;
return head->next;
}
};
|
图解:
146. LRU缓存机制
运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制。它应该支持以下操作: 获取数据 get 和 写入数据 put 。
获取数据 get(key) - 如果密钥 (key) 存在于缓存中,则获取密钥的值(总是正数),否则返回 -1。
写入数据 put(key, value) - 如果密钥不存在,则写入其数据值。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最近最少使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
进阶:
你是否可以在 O(1) 时间复杂度内完成这两种操作?
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| LRUCache cache = new LRUCache( 2 /* 缓存容量 */ );
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
cache.get(1); // 返回 1
cache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得密钥 2 作废
cache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
cache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得密钥 1 作废
cache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
cache.get(3); // 返回 3
cache.get(4); // 返回 4
|
思路详解:
要让 put 和 get 方法的时间复杂度为 O(1)O(1),我们可以总结出 cache 这个数据结构必要的条件:查找快,插入快,删除快,有顺序之分。
因为显然 cache 必须有顺序之分,以区分最近使用的和久未使用的数据;而且我们要在 cache 中查找键是否已存在;如果容量满了要删除最后一个数据;每次访问还要把数据插入到队头。
那么,什么数据结构同时符合上述条件呢?哈希表查找快,但是数据无固定顺序;链表有顺序之分,插入删除快,但是查找慢。所以结合一下,形成一种新的数据结构:哈希链表。
LRU 缓存算法的核心数据结构就是哈希链表,双向链表和哈希表的结合体。这个数据结构长这样:
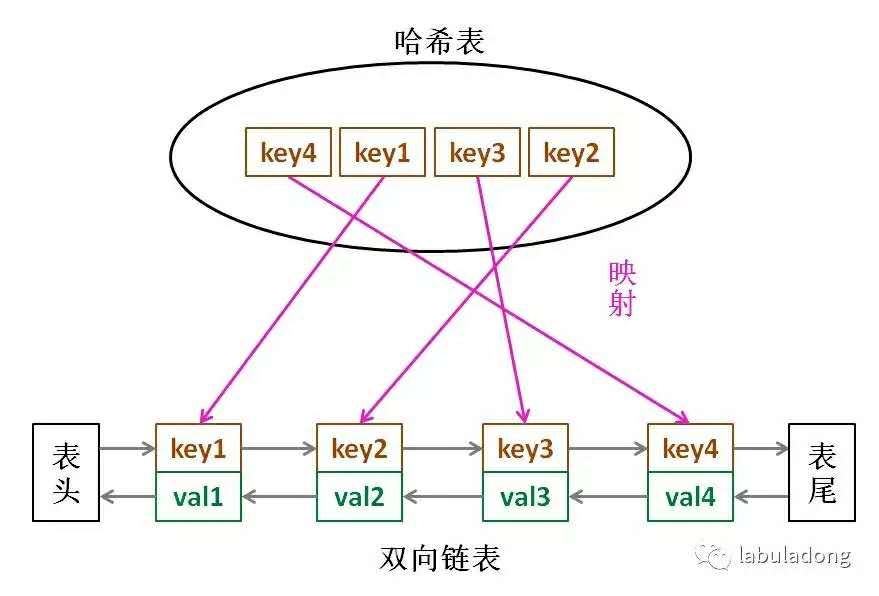
思想很简单,就是借助哈希表赋予了链表快速查找的特性嘛:可以快速查找某个 key 是否存在缓存(链表)中,同时可以快速删除、添加节点。回想刚才的例子,这种数据结构是不是完美解决了 LRU 缓存的需求?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| class LRUCache {
private:
int cap;
list<pair<int, int>> cache;
unordered_map<int, list<pair<int, int>>::iterator> map;
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) {
this->cap = capacity;
}
int get(int key) {
auto it = map.find(key);
if(it == map.end()) {
return -1;
}
pair<int, int> kv = *map[key];
cache.erase(map[key]);
cache.push_front(kv);
map[key] = cache.begin();
return kv.second;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
auto it = map.find(key);
if(it == map.end()) {
if(cache.size() == cap) {
auto lastPair = cache.back();
int lastKey = lastPair.first;
map.erase(lastKey);
cache.pop_back();
}
cache.push_front(make_pair(key, value));
map[key] = cache.begin();
} else {
cache.erase(map[key]);
cache.push_front(make_pair(key, value));
map[key] = cache.begin();
}
}
};
|
149. 直线上最多的点数
给定一个二维平面,平面上有 n 个点,求最多有多少个点在同一条直线上。
示例 1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| 输入: [[1,1],[2,2],[3,3]]
输出: 3
解释:
^
|
| o
| o
| o
+------------->
0 1 2 3 4
|
示例 2:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| 输入: [[1,1],[3,2],[5,3],[4,1],[2,3],[1,4]]
输出: 4
解释:
^
|
| o
| o o
| o
| o o
+------------------->
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
|
思路:
针对每一个点,利用hashmap,然后遍历每一个点,计算斜率,利用hashmap检查该斜率是否已经出现过,然后更新hashmap
这里需要注意的是精度问题!因为斜率计算的时候是double类型。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| class Solution {
public:
int maxPoints(vector<vector<int>>& points) {
if(points.size() <= 2) {
return points.size();
}
map<long long, int> mp;
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < points.size();i++) {
mp.clear();
int col = 1, tp = 0;
for(int j = i + 1;j < points.size();j++) {
int dely = points[j][1] - points[i][1];
int delx = points[j][0] - points[i][0];
if(delx == 0 && dely == 0) {
col++;
continue;
}
int gcd = __gcd(delx, dely);
dely = dely / gcd;
delx = delx / gcd;
long long hash = 1ll * delx * 1000000 + dely;
if(mp.count(hash) == 0) {
mp[hash] = 1;
tp = max(tp, mp[hash]);
} else {
mp[hash]++;
tp = max(tp, mp[hash]);
}
}
ans = max(ans, tp + col);
}
return ans;
}
};
|
152. 乘积最大子序列
给定一个整数数组 nums ,找出一个序列中乘积最大的连续子序列(该序列至少包含一个数)。
示例 1:
1
2
3
| 输入: [2,3,-2,4]
输出: 6
解释: 子数组 [2,3] 有最大乘积 6。
|
示例 2:
1
2
3
| 输入: [-2,0,-1]
输出: 0
解释: 结果不能为 2, 因为 [-2,-1] 不是子数组。
|
思路:这里还是才有用动态规划的思路,但是需要注意,仅仅用一个dp是不够的,因为你可能遇到的是如下数据:
[-2,3,-4]
如果只有一个dp[],则你记录下的dp[]的值为[-2,3,3]
因为忽略了负数乘以负数得到最大值的情形,,因此下面的方法记录了两个dp数组,分别是dpmin[],dpmax,这样,就可以顺利解决刚刚的bug了。
Code如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| class Solution {
public:
int maxProduct(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() == 1) {
return nums[0];
}
int ans = nums[0];
vector<int> dpmax(nums.size(), 0);
vector<int> dpmin(nums.size(), 0);
dpmax[0] = ans;
dpmin[0] = ans;
for(int i = 1;i < nums.size();i++) {
dpmax[i] = max(dpmax[i - 1] * nums[i], max(dpmin[i - 1] * nums[i], nums[i]));
dpmin[i] = min(dpmin[i - 1] * nums[i], min(dpmax[i - 1] * nums[i], nums[i]));
ans = max(ans, dpmax[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};
|
155. 最小栈
设计一个支持 push,pop,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
push(x) – 将元素 x 推入栈中。
pop() – 删除栈顶的元素。
top() – 获取栈顶元素。
getMin() – 检索栈中的最小元素。
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| MinStack minStack = new MinStack();
minStack.push(-2);
minStack.push(0);
minStack.push(-3);
minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -3.
minStack.pop();
minStack.top(); --> 返回 0.
minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -2.
|
思路:
一般来说,为了做到提取最小值,一般采用的是O(n)的做法,但是,为了做到O(1)的解法,我们可以有以下思路:
就是在每一次push的时候push两个值,一个是当前的x,另一个是当前的最小值,而push进去的最小值只需要在之前的最小值和x之间选择较小的一个即可。pop的时候同理,每次pop两个元素。而这样在去的最小值的时候,可以直接取栈顶元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| class MinStack {
private:
int index = -1;
int length;
int nums[20000];
public:
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
nums[++index] = x;
if(index == 0) {
nums[++index] = x;
} else {
nums[++index] = min(x, nums[index - 1]);
}
}
void pop() {
index -= 2;
}
int top() {
return nums[index - 1];
}
int getMin() {
return nums[index];
}
};
|

